Automation is the technological upgradation of machines that require minimal human input. Here the software takes over the human brains by applying artificial intelligence (AI).
Since it has minor human interference keeping the whole system under surveillance and security is also essential indeed. Assailants are nowadays using automation for fast mobility, installing new dangers rapidly.
Top-notch security systems are a need as the cyber threats confronted by every business or defense organization are heightening every second. Establishing a security device system is the only solution to keep the deck clean and safe every time.
Streamlining security device management is crucial and inevitable for every work area or industry. This competitive world has demanded highly equipped IT security against any IT threat.
Definition Of Threat

A report of these hazards is needed to create an automation strategy to be toughened against safety hazards. The web assaulter’s features may rank dangers, terrifying features, the attack, the attack’s goal, and the system exposure to the danger’s prey. Detractors may be described as:
- Inexpert – who breaks into techniques for silliness and credit. Hard to control, but the impacts are ignoble.
- Skilled hackers – crack into systems to rob useful assets or on an agreement basis. Extremely challenging to handle, results are usually economic. May be employed to execute robbery, industrial espionage, or sabotage
- Nation’s NGOs – bust into methods to collect brilliance, sabotage competitors’ goods, or force societal upheaval.
- The unwanted malware is an automated attack software. Plan goes from creating botnets for additional seizures, stealing, or widespread disorder—from comfortable to hold to somewhat tough to handle.
- Unhappy employees: They are risky if they join the threat team as they may know many security codes and passwords of the whole system, which can lead to severe cyber destruction.
How To Characterize The Attacks
- Denial of service – functions disrupted by a vast number of pest messages on the web, delaying or stopping honest web gridlock
- Storage change – forces the computer to run the assailant’s program.
- Memory edit – substitutes parts of running program with assailant’s program
- Memory Injection
- SQL injection
- “Man-in-the-Middle” – assailant mimics a trusted computer, inserting itself as a middleman between trusted member computers, changing the messages between them to achieve the attacker’s goals.
- Web monitoring – scans messages between systems to complete system information.
- Escalation of ownership – gives assailant organizational advantages in the system.
- Phishing raids – persuading users to unknowingly install malware by clicking on links, missing outward-directed firewalls
- Social engineering – assailants manipulate, relying on, helpful notions of plant personnel to gain information used to avoid defenses
- The material transformation or deliberate destruction of the control equipment
Best Automation Security Available

Different automation safety guards are known but only effective against some types of attackers or attacks. Security procedures, methods, instruments, and software must be utilized to slow or stop cyber attacks.
Virus Scanners:
Virus scanner software can identify known malware and raid tools by recognizing habits in the code. Virus scanners usually include easy trespass detection systems, watching for questionable activity on docks and net browsers.
Virus scanners are helpful against the known world of viruses and are needed in automation techniques. However, if caught, hackers test manipulations against all essential virus scanners and change routines.
For this reason, virus scanners are usually weak against hackers. Virus scanners must be revised frequently to identify new malware practices.
Firewalls:
Firewalls secure transmission from unauthorized origins or classes. They are vital to maintaining undesirable internet traffic from an automation design.
Nevertheless, a firewall is only as practical as its design. The default firewall setup intercepts incoming data requests but does not stop outgoing data demands and incoming replies.
This system produces inadequately configured firewalls weak to phishing episodes. Designing firewalls is not an effortless job and is not a talent established that most control engineers maintain
Allow Listing:
Allowlists arrive from the other order, precluding all programs not counted to an allowlist by an approved user. This approach would prevent all attacks from operating on a computer employing allow listing.
Allowlisting software often also contains memory safety instruments to block memory transformation attacks. Allowlisting is effective against most storage conversion attacks and some memory transformation attacks.
IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems):
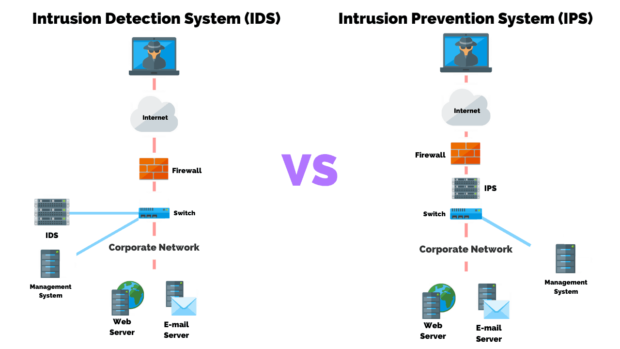
Physical intrusion detection systems use cameras and detectors to detect and record access to covered physical methods such as the factory floor or cupboards containing automation equipment. Web trespass detection systems scan network gridlock for abnormal movement and enter any they locate.
Passwords & Identification:
Passwords and other identification tools are the most generally used data protection agencies in almost all computer techniques and automation machines. Nonetheless, password tools have a vital flaw. But individuals need to be sounder at recognizing them. In expansion, many automation and networking appliances use a small set of passwords linked to a license level, not to a user.
Software Updating:

Attackers use bugs and directions in system software to achieve unapproved access to methods and information. System software factories frequently broadcast updates to release learned susceptibilities.
Establishing these updates locks protection exposures, particularly storage change, memory advancement, and right escalation seizures. Yet, it may also “smash” automation systems by altering how system services are designed.
Physical Pass Control:
Detractors who can achieve a physical pass to a mechanization system can avoid web-based protective actions to influence the managed process. This safety mechanism can be as easy as disjoining or carrying wires or as complicated as counting logic bombs to the control programs.
Physical entry to the dominion system can also permit assailants to locate password records, copy information, and swipe arduous crusades. Locks, cameras, and physical intrusion notifications can prevent physical access attacks.
Media Key Control:
In addition to web and physical invasions, cyberpunks can employ malware living on storage media to strike systems.
Take Away
The automation techniques have depended on protection through anonymity to bypass computer seizures. In the old days, the number of cyber attacks on automation techniques were feeble. The entire scenario has changed now because of great transformations in technology. Nowadays the tools needed to conduct these attacks are easily accessible and aggressive in nature. So it is important to acquire advanced safety measures to confront invasions in the coming future. Accurate formatting of safety choices on power system tools can pitch other obstacles to web raids.

